Characterization for optimizing the integrated management of solid waste for energy recovery and circular economy

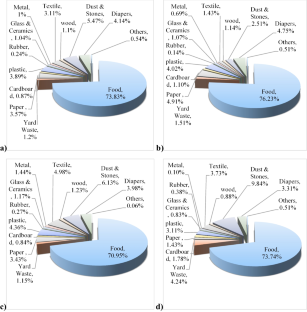
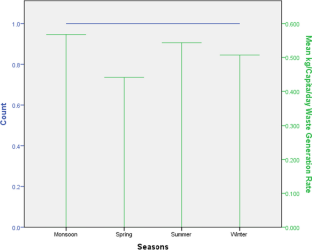
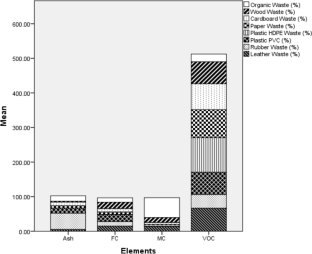
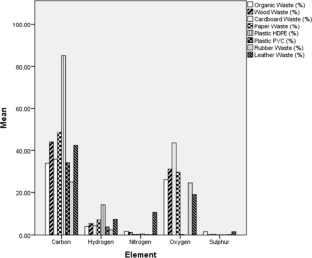
Municipal solid waste (MSW) management poses a significant environmental challenge in municipalities across developing nations worldwide. Our studies were focused on characterizing the waste and analyzing the chemical properties of mixed waste fractions to assess their potential for waste-to-energy conversion. The objective of our study was to scrutinize the existing state of the MSW management system and gauge its waste generation rates. Specific ASTM methods were employed to carry out both physical and chemical characterizations. The outcomes reveal that the city generates a daily volume of 1155 tons of domestic solid waste (DSW), translating to a generation rate of 0.51 kg −1 capita −1 day −1 . When analyzed by source, organic matter emerged as the predominant constituent, accounting for 73.74% of the waste, followed by combustible content waste at 15.17%. The moisture content of MSW ranged between 26 and 58% throughout the seasons, while volatile solids varied from 22.35 to 99.74%. Among the components screened, carbon and oxygen stood out as the dominant elements. The calorific values encompassed a broad range, ranging from 14.87 MJ kg −1 for leather waste to a substantial 25,629.27 MJ kg −1 for organic waste. To alleviate the escalating burden of increasing solid waste generation, alternative treatment approaches were recommended. These include composting, biomethane plants, the establishment of recycling facilities, and the enhancement of existing landfill sites to scientifically designed landfills. In summary, the findings from this study provide valuable insights for regulatory bodies and municipal authorities. These insights can guide the formulation of policies concerning waste sampling, characterization, segregation, and the implementation of education and awareness campaigns.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Similar content being viewed by others
Characterization and sustainable management strategies of municipal solid waste in Egypt
Article 12 June 2020

Practices of Solid Waste Processing and Disposal
Chapter © 2021
A review of municipal solid waste in China: characteristics, compositions, influential factors and treatment technologies
Article Open access 09 September 2020
Explore related subjects
Data availability
Entire data generated in this experiment has been included in this manuscript.
References
- Abu Qdais HA (2007) Techno-economic assessment of municipal solid waste management in Jordan. Waste Manag 27(11):1666–1672 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Akmal T, Jamil F (2021) Assessing health damages from improper disposal of solid waste in metropolitan Islamabad-Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Sustainability 13(5):2717 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- ASTM International (2004a) Test method for ash in the analysis sample of refuse derived fuel; ASTM-E830–87; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 778–783
- ASTM International (2004b) Test method for total moisture in a reused derived fuel laboratory sample; ASTM-E949–88; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 839–842
- ASTM (2019) Standard test method for volatile matter in the analysis of particulate wood fuels, E872–82. ed. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: American Society for Testing and Materials
- Baawain M, Al-Mamun A, Omidvarborna H, Al-Amri W (2017) Ultimate composition analysis of municipal solid waste in Muscat. J Clean Prod 148:355–362 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Batool SA, Chuadhry MN (2009) The impact of municipal solid waste treatment methods on greenhouse gas emissions in Lahore, Pakistan. Waste Manag 29(1):63–69 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Bhat RA, Nazir R, Ashraf S (2014) Municipal solid waste generation rates and its management at Yusmarg forest ecosystem, a tourist resort in Kashmir. Waste Manag Res 32:165–169 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Boumanchar I, Chhiti Y, Alaoui FEM, Sahibed-Dine A, Bentiss F, Jama C, Bensitel M (2018) Municipal solid waste higher heating value prediction from ultimate analysis using multiple regression and genetic programming techniques. Waste Manag Res 37:578–589 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Buenrostro O, Bocco G, Bernache G (2001) Urban solid waste generation and disposal in Mexico: a case study. Waste Manag Res 19(2):169–176 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
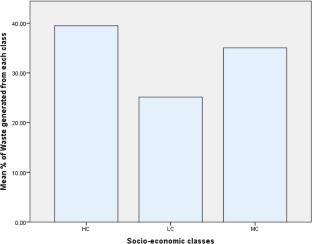
- Cheela VRS, Goel S, John M, Dubey B (2021) Characterization of municipal solid waste based on seasonal variations, source and socio-economic aspects. WDSE 3:275–288 Google Scholar
- Dangi MB, Pretz CR, Urynowicz MA, Gerow KG, Reddy JM (2011) Municipal solid waste generation in Kathmandu Nepal. J Environ Manag 92:240–249 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Dlamini S, Simatele MD, Serge Kubanza N (2019) Municipal solid waste management in South Africa: from waste to energy recovery through waste-to-energy technologies in Johannesburg. Local Environ 24:249–257 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Faisalabad Waste Management Company (FWMC) (2015). Action plan to expand solid waste management services to the entire city area
- Ferronato N, Torretta V (2019) Waste mismanagement in developing countries: a review of global issues. Int J Environ Health Res 16:1060 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Golhosseini Z, Jalili Ghazizadeh M (2021) Municipal solid waste status in Iran; from generation to disposal. Preprint available at Research Square 1–17.
- Hussain F, Chaudhry MN, Batool SA (2014) Assessment of key parameters in municipal solid waste management: a prerequisite for sustainability. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 21(6):519–525 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ilyas H, Ilyas S, Ahmad S, Nawaz M (2017) Waste generation rate and composition analysis of solid waste in Gujranwala City Pakistan. Int J Waste Resour 7(297):2 Google Scholar
- Iqbal A, Abdullah Y, Nizami AS, Sultan IA, Sharif F (2022) Assessment of solid waste management system in pakistan and sustainable model from environmental and economic perspective. Sustainability 14(19):12680 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Jabeen FM, Yamin M, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Batool SA, Mahmood A, Khalid S (2021) Estimation of greenhouse gases emission from domestic solid waste of Faisalabad city and its proposed chemical formula. Pakistan J Agric Sci 58:69–79 Google Scholar
- Jabeen F, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Mahmood A, Khalid S, Sipra HFK, Bokhari A, Mubashir M, Khoo KS, Show PL (2022) Trash to energy: a measure for the energy potential of combustible content of domestic solid waste generated from an industrialized city of Pakistan. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 137:104223 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Jadoon A, Batool SA, Chaudhry MN (2014) Assessment of factors affecting household solid waste generation and its composition in Gulberg Town, Lahore, Pakistan. J Mater Cycles Waste Managt 16:73–81 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Jerin DT, Sara HH, Radia MA, Hema PS, Hasan S, Urme SA, Audia C, Hasan MT, Quayyum Z (2022) An overview of progress towards implementation of solid waste management policies in Dhaka. Bangladesh Heliyon 8:08918 Google Scholar
- Joel W, Eckart R (1986) Modern power plant engineering, 2nd edition, Prentice- Hall International, New Delhi
- Johari A, Hashim H, Mat R, Alias H, Hassim M, Rozzainee M (2012) Generalization, formulation and heat contents of simulated MSW with high moisture content. J Eng Sci Technol 7(6):701–710 Google Scholar
- Kabera T, Wilson DC, Nishimwe H (2019) Benchmarking performance of solid waste management and recycling systems in East Africa: comparing Kigali Rwanda with other major cities. Waste Manag Res 37:58–72 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Kamran A, Chaudhry MN, Batool SA (2015) Effects of socio-economic status and seasonal variation on municipal solid waste composition: a baseline study for future planning and development. Environ Sci Eur 27:16 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Kaza S, Yao L, Bhada-Tata P, Van Woerden F (2018) What a Waste 2.0: a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050; The World Bank:1–296
- Khan D, Kumar SR, Samadder (2016) Impact of socioeconomic status on municipal solid waste generation rate. Waste manag 49:15–25 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Kumar S, Pandey A (2019) Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering and waste treatment processes for energy generation: an introduction. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands:1–9
- Lagerkvist A, Dahlen L (2019) Solid waste generation and characterization. In Recovery of materials and energy from urban wastes: a volume in the encyclopedia of sustainability science and technology, 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland:7–20
- Lee C, Huffman G (2001) Solid waste calculations: thermodynamics used in environmental engineering. Handbook Incineration 2(2):47 Google Scholar
- Macrae G (2012) Solid waste management in tropical Asia: what can we learn from Bali? Waste Manag Res 30:72–79 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mahar A, Malik RN, Qadir A, Ahmed T, Khan Z, Khan MA (2019) Review and analysis of current solid waste management situation in urban areas of Pakistan. In Proceedings of the Inter-National Conference on Sustainable Solid Waste Management, Chennai, India, 10–11:34–41
- Moftah WAS, Marković D, Moftah OAS, Naseef L (2016) Characterization of household solid waste and management in Tripoli City—Libya. Open J Ecol 6:435–442 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mushtaq J, Dar AQ, Ahsan N (2020) Physio-chemical characterization of municipal solid waste and its management in high-altitude urban areas of North-Western Himalayas. WDSE 2:151–160 Google Scholar
- Nabavi-Pelesaraei A, Bayat R, Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha H, Afrasyabi H, Chau KW (2017) Modelling of energy consumption and environmental life cycle assessment for incineration and landfll systems of municipal solid waste management—a case study in Tehran Metropolis of Iran. J Clean Prod 148:427–440 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Olley JE, Jgosse J, Rudin V, Alabaster G (2014) Developing a common framework for integrated solid waste management advances in Managua Nicaragua. Waste Manag Res 32:822–833 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis, handbook of chemical and microbiological properties –part 2 (second edition)
- Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (2017) Provisional summary results of 6th population and housing census-2017
- Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, Government of Pakistan. Available online: https://www.pbs.gov.pk/content/population-census. accessed on 1 September 2022
- Permana AS, Towolioe S, Abd Aziz N, Ho CS (2015) Sustainable solid waste management practices and perceived cleanliness in a low-income city. Habitat Int 49:197–205 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Pokhrel D, Viraraghavan T (2005) Municipal solid waste management in Nepal: practices and challenges. Waste Manage 25:555–562 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Ramakrishna V, Subrahmanyam CN, Bhanuchand S (2016) Municipal solid waste quantification, characterization and management in Mylavaram. IOSR J Mech Civ Eng 13:77–87 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Romano G, Rapposelli A, Marrucci L (2019) Improving waste production and recycling through zero-waste strategy and privatization: an empirical investigation. Resour Conserv Recycl 146:256–263 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Semernya L, Ramola A, Alfthan B (2017) Waste management outlook for mountain regions: sources and solutions. https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/16794. Accessed 28 Aug 2019
- Serge Kubanza N, Simatele MD (2020) Sustainable solid waste management in developing countries: a study of institutional strengthening for solid waste management in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Environ Plan Manag 63:175–188 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sethi S, Kothiyal NC, Nema AK, Kaushik MK (2013) Characterization of municipal solid waste in Jalandhar City, Punjab, India. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 17(2):97–106 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Sohoo I, Ritzkowski M, Sohu ZA, Cinar SÖ, Chong ZK, Kuchta K (2021) Estimation of methane production and electrical energy generation from municipal solid waste disposal sites in Pakistan. Energies 14:2444 ArticleCASGoogle Scholar
- Soukiazis E, Proença S (2020) The determinants of waste generation and recycling performance across the Portuguese municipalities – a simultaneous equation approach. Waste Manage 114:321–330 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sukarni S (2016) Exploring the potential of municipal solid waste (MSW) as solid fuel for energy generation: case study in the Malang City, Indonesia. AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing LLC: 020003
- Suthar S, Singh P (2015) Household solid waste generation and composition in different family size and socio-economic groups: a case study. Sustain Cities Soc 14:56–63 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- SWM Rules (2016) Municipal solid waste management manual-part II. Minist Urban Dev 3:604 Google Scholar
- Tabatabai MA (1974) Determination of sulphates in water samples. Sulphur Inst J 10:11–13 CASGoogle Scholar
- Zia A, Batool SA, Chauhdry MN, Munir S (2017) Influence of income level and seasons on quantity and composition of municipal solid waste: a case study of the capital city of Pakistan. Sustainability 9:1–13 ArticleGoogle Scholar
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Government College University Faisalabad Pakistan for all the support to coduct this experimental work.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan via project number HEC-NRPU 5635. The authors are grateful to HEC for this research funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Environmental Sciences, Abdul Wali Khan University, Mardan, Pakistan Fariha Jabeen & Uzma Noreen
- Department of Environmental Sciences, Government College University Faisalabad, Faisalabad, 38000, Pakistan Fariha Jabeen, Muhammad Adrees, Muhammad Ibrahim & Abid Mahmood
- Department of Environmental Sciences, Kohat University of Science and Technology, Kohat, 26000, Pakistan Muhammad Waqas
- Department of Environmental Sciences, University of Jhang, Jhang, Pakistan Afifa Aslam
- Fariha Jabeen










