
Property and casualty (P&C) insurers are companies that provide coverage on assets (e.g., house, car, etc.) and also liability insurance for accidents, injuries, and damage to other people or their belongings.

Outlined in the Canadian Institute of Actuaries, property and casualty insurers focus on risks that result in losses to property and possessions. Examples include:
The following are several scenarios in which property and casualty insurance provide coverage:
Josh, an insured individual, forgets to shovel his front yard after a snowy day and causes a stranger to fall and fracture their leg. The property and casualty insurer can help John cover the medical costs related to the stranger, as well as damages for pain and suffering.
Tim, an insured individual, comes home to find his property vandalized. The property and casualty insurer can help Tim cover the cost related to repairing the damage done to the property.
Dan, an insured individual, lives in Florida, and his property was damaged due to a hurricane recently. The property and casualty insurer can help Dan cover the costs related to damage to the property.
Property and casualty insurers offer insurance to customers for risks, up to a certain coverage amount, in exchange for insurance premiums. Insurance premiums are cash outflows made by the customer in exchange for insurance coverage.
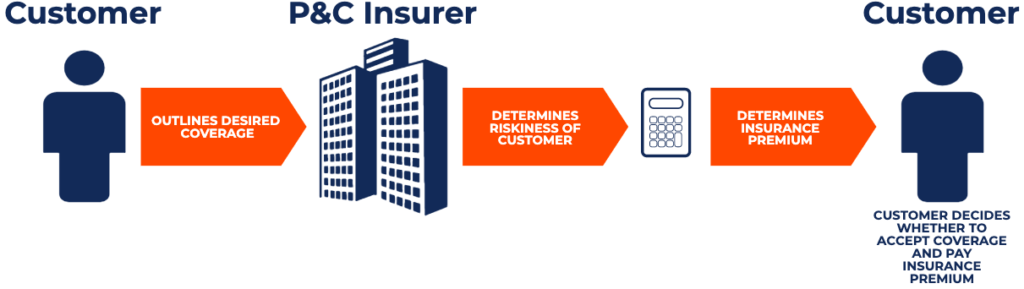
Similar to other insurers, when property and casualty insurers offer coverage to a customer, they must determine an insurance premium the customer will pay by looking at the riskiness of the customer. An insurer would commonly look at the likelihood of the customer making a claim and the potential amount of the claim when calculating the amount of insurance premium they should charge. A diagram is provided below to outline the process:
CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful: